Key Takeaways
- Giant sequoias have the largest volume and mass while redwoods are taller.
- Sequoias have massive, barrel-shaped trunks compared to redwoods’ narrower trunks.
- Sequoias grow wider leaves and larger cones than redwoods.
- Redwoods can reach over 350 feet in height, while sequoias grow up to 311 feet.
- Both trees can live over 2,000 years, with sequoias being some of the oldest trees.
- Sequoias are only found naturally in California’s Sierra Nevada mountains.
- Redwoods grow along the Pacific Coast from California to Oregon.
Introduction
Giant sequoias and coast redwoods are among the most massive and ancient tree species on Earth. These evergreen conifers are renowned for their towering heights, immense trunk girths, and longevity spanning millennia. But when it comes to size, are sequoias or redwoods bigger?
This comprehensive article will analyze the key differences between giant sequoias (Sequoiadendron giganteum) and coast redwoods (Sequoia sempervirens). Detailed comparisons of height, trunk volume, leaves, cones, and overall appearance will reveal which tree rightly deserves the title of the “largest.” Relevant facts, statistics, and research will quantify the superlative size of these ancient titans.
By the end, you will have a clear understanding of how sequoias and redwoods differ in their massive dimensions. This will settle the debate over which magnificent tree is greater in overall stature and scale. The awe-inspiring sizes of these iconic conifers will give you an appreciation for the grandeur of the natural world.

Height Comparison: Do Sequoias or Redwoods Grow Taller?
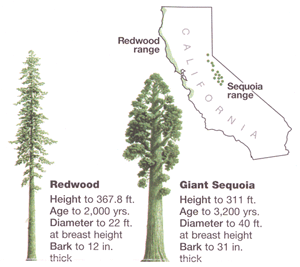
When it comes to height, coast redwoods are considered the tallest trees in the world. The tallest coast redwood ever measured reached a towering height of 379 feet (115.5 meters). This specimen, named Hyperion, was discovered in 2006 in California’s Redwood National Park.
In contrast, giant sequoias typically reach heights between 160-311 feet (49-95 meters). The tallest giant sequoia ever recorded was 326 feet (99.4 meters) tall. Though impressively tall, sequoias do not surpass coast redwoods in terms of maximum tree height.
Why are Redwoods Taller than Sequoias?
The differences in height between coast redwoods and giant sequoias arise from variations in their morphology and growing conditions:
- Narrow trunks: Coast redwoods have vertically oriented branches and narrow, conical trunks. Their tall, slender trunks allow redwoods to attain record heights. Sequoias have much wider, massive trunk bases that support horizontal branches.
- Fast growth: Redwoods grow very rapidly when young, averaging up to 3 feet per year. Their fast initial growth helps them outcompete other trees for sunlight. Sequoias grow more slowly and steadily.
- Climate: Coastal fog and mild temperatures promote rapid growth in redwoods. The arid mountain habitat of sequoias slows their growth rate.
- Competition: In dense old-growth forests, redwoods race to reach sunlight above the canopy. Sequoias grow in more open groves with less competition.
So while coast redwoods stand taller above the forest floor, giant sequoias still achieve impressive heights through their ancient, gradual growth.
Trunk Size Comparison: Do Sequoias or Redwoods Have Bigger Trunks?
When it comes to sheer trunk mass and volume, giant sequoias reign supreme as the largest trees in the world. The trunks of mature giant sequoias can exceed 30 feet in diameter. Measurements of tree volume and mass include the bulk of wood in the entire trunk.
By these metrics, the largest known giant sequoia is General Sherman tree located in Sequoia National Park. General Sherman has:
- A base circumference of 102.6 feet (31.3 meters).
- A volume of 52,508 cubic feet (1,487 cubic meters).
- An estimated mass of 1,385 tons (1,259 metric tons).
These statistics make General Sherman the most massive individual tree on Earth. The trunks of giant sequoias can grow so expansive due to the immense strength and durability of their fibrous wood.
Coast redwood trunks, while still enormous, are narrower than giant sequoias. The trunk diameters of mature redwoods average between 15-25 feet. Their more slender trunks allow redwoods to grow exceptionally tall, but limits their total wood volume compared to the bulky sequoias.
Why Sequoias Have More Massive Trunks
Several structural and environmental factors contribute to the massive trunks of giant sequoias compared to coast redwoods:
- Trunk shape: Sequoias have barrel-shaped trunks with slight taper. Redwood trunks taper more sharply.
- Branching pattern: Sequoias support heavy, horizontal branches that demand thicker trunks. Redwood branches grow vertically.
- Wood density: Sequoia wood has a lower density, allowing faster growth of trunk girth.
- Fire resistance: Thick bark protects sequoia trunks from wildfires. Redwoods are also fire-adapted but lack the same trunk protection.
- Moisture: The arid climate of sequoias’ Sierra Nevada range limits height growth, favoring expansion of trunk girth over height.
So while coast redwoods stand taller, giant sequoias clearly take the prize for the largest trunk diameters and wood volumes on Earth.
Leaf Comparison: How Do Sequoia and Redwood Leaves Differ?
Giant sequoias and coast redwoods both produce leaves that are evergreen, needle-like, and arranged spirally on twigs. But differences in the size, shape, and color of their foliage creates a distinct appearance:
Sequoia Leaves
- Shape: Flattened, blunt-tipped, and scale-like. The leaves are arranged closely along the twig.
- Length: 0.12 – 0.25 inches (3 – 6 mm) long.
- Color: Blue-green with two pale white lines running the length of the underside.
Redwood Leaves
- Shape: Pointed and awl-shaped. The leaves spread out from the twig.
- Length: 0.4 – 1 inch (10 – 25 mm) long.
- Color: Deep green on both sides.
The smaller, blue-green sequoia leaves contrast with the larger, deep green foliage of coast redwoods. These leaf traits help distinguish the two species. Their leaf sizes also correspond to differences in climate between their respective native ranges.
- Which Immunoglobulin Is Present in Breast Milk?
- What Is Educators Rising??
- Is It Straight Laced or Strait Laced?
Cone Comparison: How Do Sequoia and Redwood Cones Differ?
The cones and seeds produced by giant sequoias are significantly larger than coast redwood cones. These differences reflect the higher productivity and fertility of sequoia trees.
Sequoia Cones
- Shape: Short, bluntly rounded cones with loose, flaky scales.
- Size: Mature cones measure 3-4 inches (8-10 cm) long and 2-3 inches (5-8 cm) wide.
- Seed size: 200-300 tiny winged seeds inside each cone, about 0.1 inches (2-3 mm) long.
Redwood Cones
- Shape: Oval, egg-shaped cones with closely overlapping scales.
- Size: Mature cones measure 0.6–1 inches (1.5–2.5 cm) long and 0.4-0.8 inches (1-2 cm) wide.
- Seed size: 30-90 winged seeds inside each cone, only 0.04-0.08 inches (1-2 mm) long.
The large cones and numerous seeds of giant sequoias give them exceptional reproductive capacity. The smaller redwood cones produce fewer seeds.
Growth Rate and Longevity: How Fast and Long Do They Live?
In terms of growth rate and longevity, coast redwoods and giant sequoias are both exceptionally long-lived trees. Some key facts about their life spans:
- Fast growth when young: Coast redwoods can grow up to 3 feet (91 cm) per year when young, while sequoias grow about 1 foot (30 cm) annually.
- Longevity: The oldest coast redwoods are around 2,200 years old. Giant sequoias can exceed 3,200 years in age.
- Methuselah: A 4,850 year old bristlecone pine named Methuselah holds the record for oldest tree.
- Slow growth when old: Growth rates slow to less than 0.13 feet (4 cm) per year once the trees reach maturity after a few hundred years.
- Fire resistance: Thick protective bark allows them to survive fires, contributing to longevity.
So while coast redwoods grow faster initially, giant sequoias can outlive them and all other tree species. The longevity of sequoias and redwoods is remarkable.
- For What Is Europium Used?
- What Is the Survival Rate for Turner Syndrome?
- Are Red Footed Tortoises Social?
Geographic Range: Where Do They Naturally Grow?
Giant sequoias and coast redwoods naturally grow in separate, limited ranges:
Giant Sequoia Range
- Sierra Nevada Mountains: Sequoias only naturally grow across a narrow band of the western Sierra Nevada mountains in central California.
- Elevation: They grow between 5,000-7,000 ft (1,525-2,134 m) elevation.
- Arid climate: Sequoias thrive where cool, wet winters provide moisture and dry summers limit growth.
- Limited range: Their native habitat covers just 35,614 acres across 73 groves.
Coast Redwood Range
- Pacific Coast: Redwoods grow in a narrow strip along the Pacific Coast from southwest Oregon to central California.
- Elevation: They grow at low elevations up to 2,000 ft (610 m).
- Mild climate: The moist, moderate climate from coastal fog enables fast growth.
- Narrow range: Their habitat spans approximately 1.9 million acres.
While sequoias have a smaller native range, redwoods also only grow naturally in a narrow belt along the Pacific coast. Both trees are uniquely adapted to their local climate patterns.
Appearance and Shape: How Do They Differ?
The differing trunk shapes, branching patterns, and foliage of sequoias and redwoods create distinct silhouettes:
Giant Sequoia Shape
- Conical young trees transition to domed, mushroom-shaped crowns when mature.
- Horizontal branches emerge from the top and sides of the trunk.
- Barrel-shaped trunks with very slight taper. Immensely thick trunk bases.
- Blue-green leaves give the tree a soft, bluish tone.
Coast Redwood Shape
- Pyramid shape with a spire-like crown, even when mature.
- Upward-turned branches create a narrow crown.
- Tapering trunks that are vertical and cone-shaped.
- Deep green leaves provide a bold, verdant color.
So in visual terms, sequoias have a muted blue-green color and rounded, domed shape while redwoods have a vibrant green color and tall, tapering pyramid shape.
- Does Derecho Mean Right or Straight? Unpacking the Multiple Meanings of a Versatile Spanish Word
- What Do Yeti Numbers Mean?
- When Operating a Computer, What Does a User Interact With?
In Summary: Quantifying Their Massive Scale
In conclusion, while coast redwoods stand taller than any other tree on Earth, giant sequoias have the greatest overall size and mass of any single stem tree. Key facts quantifying their superlative dimensions:
- Tallest tree: Coast redwoods can reach 379 feet (115.5 m) tall.
- Largest tree: Giant sequoias like General Sherman have over 52,000 cubic feet (1,487 m3) of volume.
- Heaviest tree: Giant sequoias can weigh over 1,385 tons (1,259 metric tons).
- Oldest trees: Giant sequoias can live over 3,200 years. Coast redwoods over 2,200 years.
- Narrow ranges: Sequoias are only native to California’s Sierra Nevada. Redwoods grow along the Pacific Coast.
While differing in shape and proportions, coast redwoods and giant sequoias are both superlatives of the plant world. No other tree exceeds their combination of towering height and immense mass accumulated from millennia of steady, ancient growth. These iconic conifers thoroughly deserve their status as the most monumental, magnificent tree species on the planet.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which tree has the biggest trunk in the world?
The giant sequoia has the biggest, most massive trunk in the world. The General Sherman giant sequoia has a trunk volume over 52,500 cubic feet (1,487 cubic meters), far exceeding the more slender trunks of coast redwoods.
How tall can giant sequoias grow?
In ideal conditions, giant sequoias can grow over 300 feet (91 meters) tall. The tallest known giant sequoia is328 feet (99.5 meters) tall. However, coast redwoods exceed this height and are considered the tallest tree species worldwide.
Why are giant sequoias so big and tall?
Several factors enable giant sequoias to become so enormous: fast juvenile growth rates, thick fire-resistant bark, drought tolerance, longevity exceeding 3,200 years, and sufficient moisture from mountain snowmelt. Their massive size allows them to resist high winds and heavy snow loads.
Where do giant sequoias grow naturally?
Giant sequoias only grow naturally along the western slopes of the Sierra Nevada mountains in central California. Their limited habitat covers just 73 groves across a narrow elevational band between 5,000-7,000 ft (1,525-2,134 m).
How long do coast redwoods live?
The oldest coast redwoods are around 2,200 years old. Methuselah, a bristlecone pine, is the oldest known living tree at 4,850 years old. Though redwoods grow faster initially, giant sequoias can outlive them with ages exceeding 3,200 years.
Why are redwood leaves different than sequoia leaves?
Redwood and sequoia leaves diverged to suit their differing native habitats. Sequoias have small, scale-like leaves with a waxy coating that minimized water loss in their arid mountain range. Redwoods have larger, broader leaves that efficiently absorb moisture from coastal fog.
Do sequoias grow faster than redwoods when young?
No, coast redwoods grow up to 3 feet (91 cm) per year when young while giant sequoias only grow about 1 foot (30 cm) annually. The fast initial growth allows redwoods to reach great heights quickly. But sequoias catch up over time and live longer.
How are sequoias and redwoods similar?
Sequoias and redwoods are both evergreen, long-lived conifers adapted to fire. They develop thick protective bark and lignotubers that allow them to resprout after fires. Both species can live over 2,000 years. Their wood contains tannins that resist decay and insect damage.
Why are sequoia cones so much larger than redwood cones?
The larger cones and seeds of giant sequoias give them higher reproductive capacity than coast redwoods. Sequoias need greater fertility to propagate successfully in their harsh mountain habitat. Coast redwoods grow in more favorable conditions and reproduce successfully with smaller cones.
- When Operating a Computer, What Does a User Interact With?
- What Is the Meaning of Costata?
- What Do Yeti Numbers Mean?
- Where Are Bootstrap Glyphicons Stored?
- What Is a Discrepant Element?
- Were Six Presidents Named James?
- Why Do Manatees Have Nails? An In-Depth Look at These Curious Traits
- Do Twins Count As Para 2?
- How Much Is Cooltone? An In-Depth Look at the Costs
- What’s an Equivalent Expression??
- How Long to Keep Cetaphil on My Face?
- Whats Motion to Compel Arbitration?
- Are Shingles Contagious?
- How to Trick Dave App?
- How to Change Light Mode on a Fantech Keyboard?
- Why does the urine smell so funny after eating asparagus?
- How to Watch Redzone on Sling TV?
- Do Terpenes Make You Cough? (Explained)
- What does the ‘Views’ feature on my Facebook Collection mean?
- Are 0 IV Pokemon Good?
- What Animals Mate for Life?
- Does Crying Burn Calories? (Detailed Guide)